#前言
本文根据《数据结构与算法JavaScript描述》来写的,相当于个人的读书笔记。
#树的简介
树是计算机科学中经常用到的数据结构。树是一种非线性的数据结构,以分层的方式存储数据,树由一组以边连接的节点组成,一个节点可以有 0、1 或多个子节点。
#与树涉及的概念
- 根节点: 一棵树最上面的节点称为根节点
- 父节点: 如果一个节点下面连接多个节点,那么该节点称为父节点
- 子节点: 父节点下面的节点称为子节点
- 叶子节点: 没有任何子节点的节点称为叶子节点
- 路径: 从树中一个节点到另一个节点的这一组边称为路径
- 树的遍历: 以某种特定顺序访问树中所有节点
- 树的深度: 根节点是第 0 层,以此类推,树的层数就是树的深度
#二叉树定义
二叉树是一种特殊的树,它的子节点个数不超过两个。二叉树具有一些特殊的计算性质,使得在他们之上的一些操作异常高效。二叉查找树是一种特殊的二叉树,相对较小的值保存在左节点中,较大的值保存在右节点中。这一特性使得查找的效率很高。
#JS 模拟二叉查找树
这里主要介绍 BST 的插入方法:
- 设根节点为当前节点
- 如果待插入节点保存的数据小于当前节点,则设新的当前节点为原节点的左节点,反之,执行第 4 步
- 如果当前节点的左节点为 null,就将新的节点插入这个位置,退出循环,反之,继续执行下一个循环
- 设新的当前节点为原节点的右节点
- 如果当前节点的右节点为 null,就将新的节点插入这个位置,退出循环,反之,继续执行下一个循环
class Node {
constructor(data, left, right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
show() {
return this.data;
}
}
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
insert(data) {
const n = new Node(data, null, null);
if (this.root === null) {
return (this.root = n);
}
let current = this.root;
let parent;
while (true) {
parent = current;
if (data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
if (current === null) {
parent.left = n;
break;
}
} else {
current = current.right;
if (current === null) {
parent.right = n;
break;
}
}
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#遍历二叉树
有三种遍历 BST 的方式: 中序、先序和后序。中序遍历按照节点上的键值,以升序访问 BST 上的所有节点。先序遍历先访问根节点,然后以同样方式访问左子树和右子树。后序遍历先访问叶子节点,从左子树到右子树,再到根节点。
#中序遍历
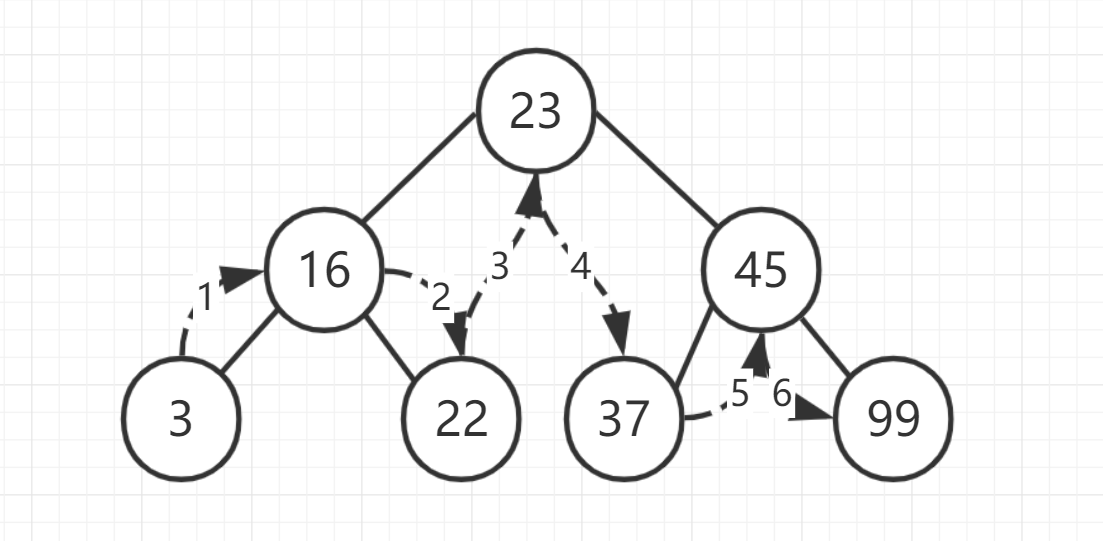
class BST {
// ...
// 左根右
inOrder(node) {
if (!(node === null)) {
inOrder(node.left);
console.log(node.show() + " ");
inOrder(node.right);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#先序遍历
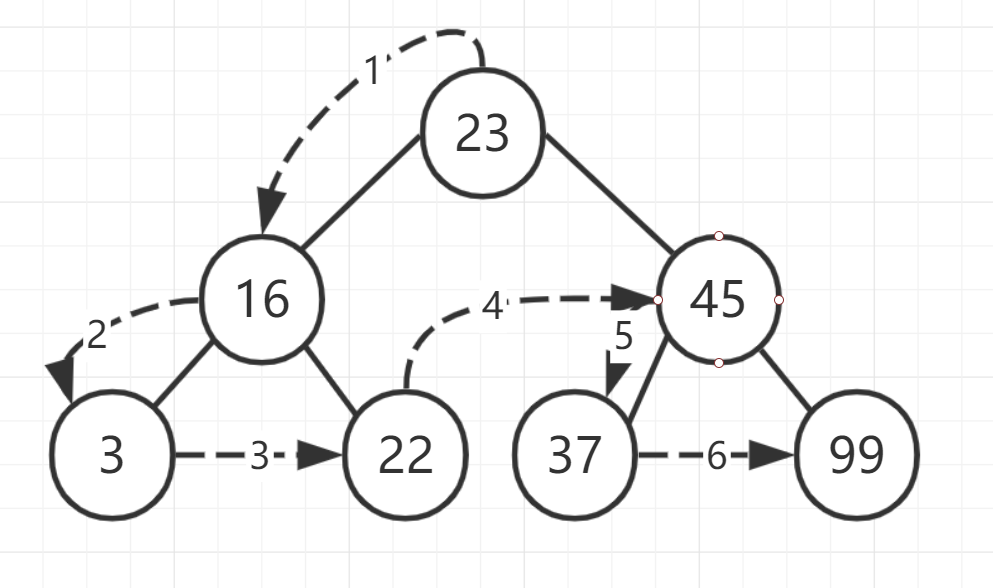
class BST {
// ...
// 根左右
preOrder(node) {
if (!(node === null)) {
console.log(node.show() + " ");
this.preOrder(node.left);
this.preOrder(node.right);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#后序遍历
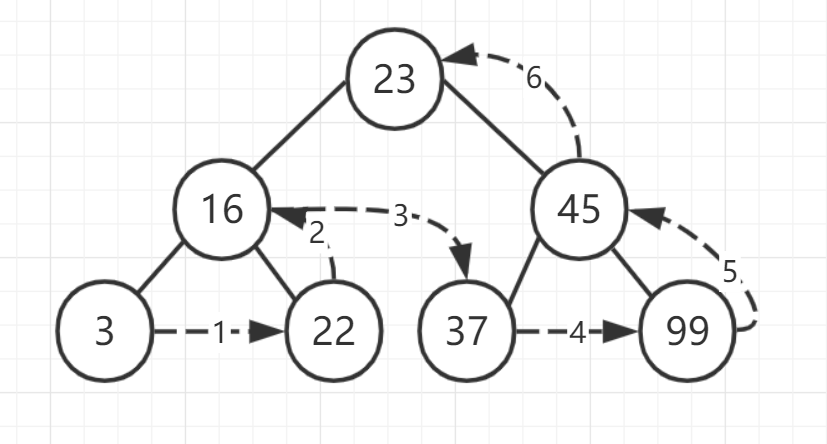
class BST {
// ...
// 左右根
posOrder(node) {
if (!(node === null)) {
this.posOrder(node.left);
this.posOrder(node.right);
console.log(node.show());
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
#测试
const nums = new BST();
nums.insert(23);
nums.insert(45);
nums.insert(16);
nums.insert(37);
nums.insert(3);
nums.insert(99);
nums.insert(21);
nums.insert(5);
nums.insert(20);
nums.insert(22);
nums.inOrder(nums.root); // 3 5 16 20 21 22 23 37 99
nums.preOrder(nums.root); // 23 16 3 5 21 20 22 45 37 99
nums.posOrder(nums.root); // 5 3 20 22 21 16 37 99 45 23
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
#元素查找
#查找最大、最小值
class BST {
// ...
getMin() {
let current = this.root;
while (!(current.left === null)) {
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
getMax() {
let current = this.root;
while (!(current.right === null)) {
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#查找给定值
class BST {
// ...
find(data) {
let current = this.root;
while (!(current === null)) {
if (current.data === data) {
return current;
} else if (data < current.data) {
current = current.left;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return null;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
#元素删除
从 BST 中删除节点的第一步是判断当前节点是否包含待删除的数据,如果包含,则删除该节点;如果不包含,则比较当前节点上的数据与待删除的数据。如果待删除数据小于当前节点的数据,则移至当前节点的左节点继续比较,反之,则移至当前节点的右节点。
如果待删除节点是叶子节点,那么只需要将父节点指向它的链接变成指向 null;如果待删除的节点只包含一个子节点,那么原本指向它的父节点指向它的子节点;如果待删除的节点包含两个子节点,正确的做法有两种,要么查找待删除节点左子树的最大值,要么查找其右子树的最小值,这里代码实现使用后一种方式。查找到最小值后,把最小值赋值到该节点,然后删除右子树的最小值。
class BST {
// ...
getSmallest(node) {
while (!(node.left === null)) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
remove(data) {
this.root = this.removeNode(this.root, data);
}
removeNode(node, data) {
if (node === null) return null;
if (data === node.data) {
// 没有子节点的节点
if (node.left === null && node.right === null) {
return null;
}
// 没有左节点的节点
if (node.left === null) {
return node.right;
}
// 没有右节点的节点
if (node.right === null) {
return node.left;
}
let tempNode = this.getSmallest(node.right);
node.data = tempNode.data;
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, tempNode.data);
return node;
} else if (data < node.data) {
node.left = this.removeNode(node.left, data);
return node;
} else {
node.right = this.removeNode(node.right, data);
return node;
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
#计数
记录一组数据出现的次数
class BST {
constructor(data, left, right) {
// ...
this.count = 1;
}
update(data) {
let node = this.find(data);
node.count++;
return true;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12